Health Improvement Card and NCD Action Toolkit
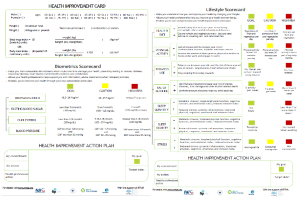
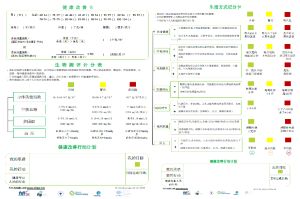
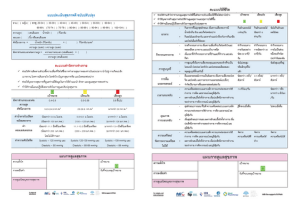
The WHPA modified Health Improvement Card (mHIC) is a tool to support positive behaviour and lifestyle changes which can reduce and prevent chronic or noncommunicable diseases (NCDs). An easy-to-use two-pager, it identifies risk factors for NCDs and suggests target actions and measurable goals for a healthier lifestyle.
It empowers individuals to work with their health professionals to establish personal health goals and track progress over time, encouraged by the written commitment to change made on the card. It provides health professionals with concise tool to prompt, support and supervise patients to reduce the risk of NCDs. It can be used by different health professions and is suitable for any income setting.
It is available in English, Chinese, Thai and Mongolian:
Download the Health Improvement Card in English
Download the Health Improvement Card in Chinese
Download the Health Improvement Card in Thai
Download the Health Improvement Card in Mongolian
The Health Improvement Card was most recently updated in 2024, adding weight-to-height measurement and body mass index as health indicators, and the targets for servings of fruit and vegetables and for alcohol use were adjusted.
The HIC was also updated in 2022 and 2023 to reflect more up-to-date data and to add sleep and stress as lifestyle factors influencing health. (1)
NCD Action Toolkit for Health Professionals, Patients and the Public (2011)
The original HIC was part of a toolkit to reduce NCDs, developed and published by WHPA in 2011. The toolkit consists of the HIC and two manuals. One manual is for patients and contains further background information on major NCD risk factors as well as advice on developing a personal plan to improve health, using the HIC in collaboration with a health professional. The other manual is for health professionals and provides guidance on how to use the HIC to work with patients on making lifestyle changes to improve their health.
Supported by research
The Chinese version of the original HIC has been tested and validated in two peer-reviewed studies.
- Yiwen Bai, Xubo Wu, Raymond CC Tsang, Ruisheng Yun, Yan Lu, Elizabeth Dean and Alice YM Jones. 2020. A Randomised Controlled Trial to Evaluate the Administration of the Health Improvement Card as a Health Promotion Tool: A Physiotherapist-Led Community-Based Initiative. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 17, 8065.
- Xubo Wu, Alice YM Jones, Yiwen Bai, Jia Han and Elizabeth Dean. 2019. Use of the Health Improvement Card by Chinese physical therapy students: A pilot study. PLoS ONE 14(9).
(1) The WHPA gratefully acknowledges the updates to the HIC by Elizabeth Dean (University of British Columbia) and her team.
©2019 World Health Professions Alliance